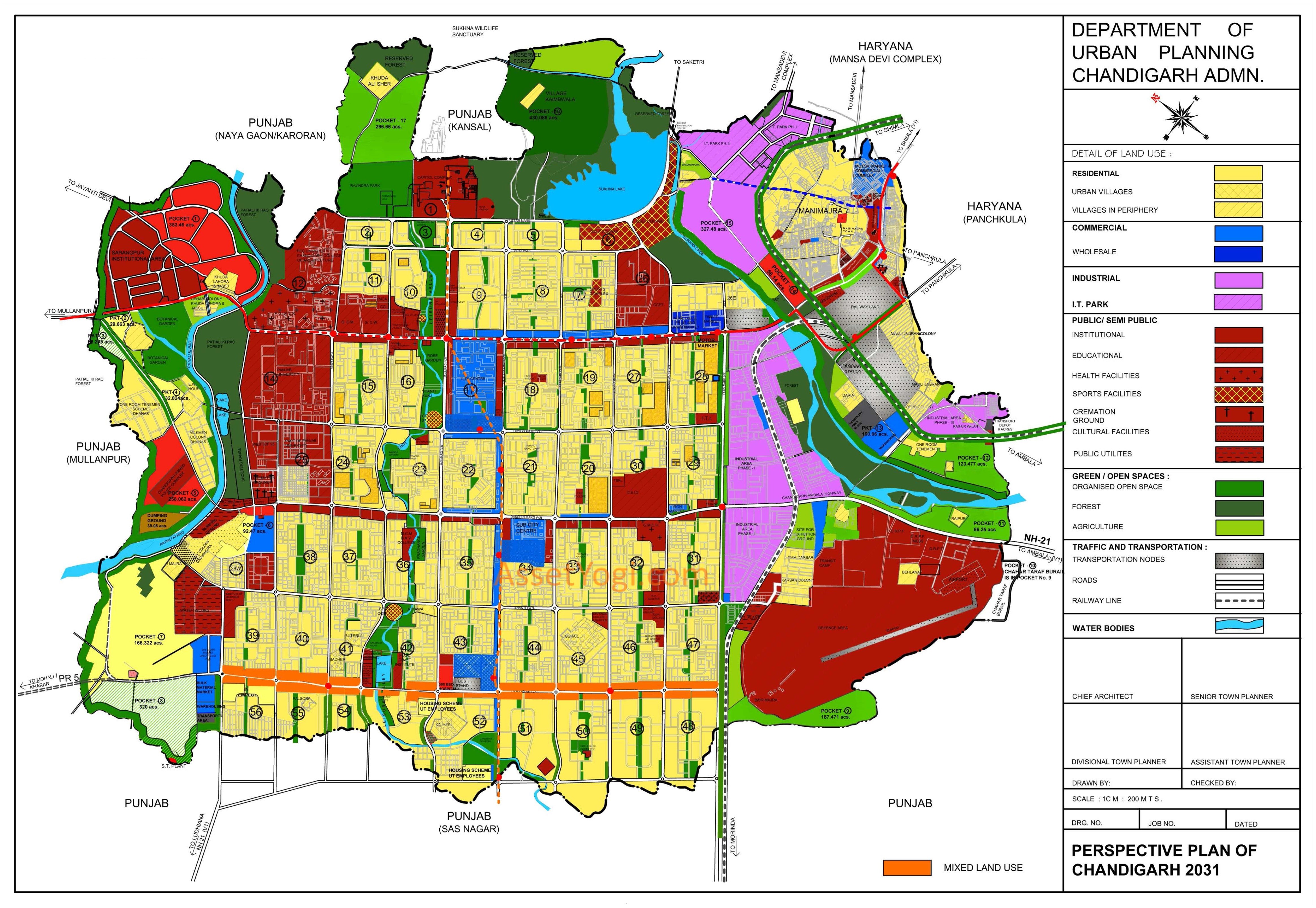
Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 (Draft) has been prepared to provide regulations for development and building activity in the entire Union Territory of Chandigarh. The planning area constitutes 144 sq km. It includes 60 sectors in the sectoral grid as well as the periphery areas outside it.
You can download the master plan of chandigarh in high quality pdf from below. You can go through the Highlights of proposed master plan, in case you don’t have enough time to go through the complete master plan. If you want to share your opinions and suggestions, please use the comments section at the end of the page.
Downloads
Master Plan 2031 – PDF Map
Highlights – Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 (Draft)
Introduction
Chandigarh is a city and a union territory in the northern part of India that serves as the capital of the states of Punjab and Haryana. As a union territory, the city is ruled directly by the Union Government of India and is not part of either state.
The city of Chandigarh was the first planned city in India post-independence in 1947 and is known internationally for its architecture and urban design. The master plan of Chandigarh was prepared by Le Corbusier, transformed from an earlier plan by the American planner Albert Mayer. Le Corbusier designed an iconic city, fulfilling not just a utopian agenda, but reflecting concepts of ‘modernism’ movement that arose in Europe but took root here too.
The original plan was divided into a grid of 30 sectors with the Capitol Complex as well as the Civic Centre as its focal points. Sector 17 was designed as the Central Business District and a greenbelt at the centre ran north east to south west.
Wide roads planned in a systematic hierarchy provide structure to the city which has well planned facilities. Landscaped green avenues give it amenity value.
Background
CHRONOLOGICAL SEQUENCE OF EVENTS
1966
Reorganisation of the State of Punjab into States of Haryana & Punjab with Chandigarh functioning as the State Capital of both. Creation of the Union Territory of Chandigarh in 70 sq km as Capital City and 26 adjoining villages in 44 sq km.
Out of the 1315 sq km extended periphery, 1021 sq km of the Periphery Control Area went to Punjab, 295 sq km to Haryana with remaining area of 114 sq km forming the UT with the Capital City for all its present and future needs. Out of this defined new periphery it was clear that Chandigarh got just 3% land of the original periphery.
Post 1966
Establishment of Mohali township of Punjab in periphery covering 5500 acres and, Panchkula township of Haryana covering 5000 acres. Townships in the periphery emerged as a result of development pressures observed in the form of unregulated growth.
1977
Preparation of the Regional Plan for Chandigarh’s immediate region. Called the ‘Chandigarh Urban Complex’ (CUC) Plan, the first Chandigarh Master Plan covered 330 sq km. It comprised of Chandigarh Union Territory (UT), parts of Mohali, its adjoining 27 villages and parts of Panchkula and 23 villages.
The CUC Plan was approved by the Co ordination Committee. The area of this plan was entirely within the originally conceptualized 8km radius periphery control belt. The CUC Plan declared the area north of the Capitol Complex as ‘No Development Zone’.
2008
Punjab Government notified ‘GMADA REGIONAL PLAN 2056’ covering 1021 sq km. This plan entailed creating 7 Integrated Economic Hubs consisting of a huge agglomeration in absolute continuity to the Chandigarh UT . These hubs would be major drivers of economic growth.
The area north of Chandigarh and abutting the Capitol Complex created by Le Corbusier and consisting of the village settlements Naya Gaon & Kansal has also been notified as a Nagar Panchayat by the Punjab Government under whose jurisdiction the land falls.
In a similar manner, the Haryana Government has planned 5 settlements, (Refer Map 12). Of these, Panchkula and the ‘Panchkula Extension-1’ across river Ghaggar stand fully developed. Panchkula Extension- 2, Shree Mata Mansa Devi Complex comprising of 1550 acres, close to Sukhna Lake and Kalka-Pinjore Urban Complex are under development.
Outlook for Chandigarh Master Plan 2031
The reorganization of states and further developments around it impose constraints on the growth of Chandigarh city. The proposed Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 respects its historical legacy and optimises on its constraints of land.
The plan is an attempt to redeem an efficient circulation network and extensive lung space as well as the scenic backdrop of the Shivalik Hills against which lies the dramatic Capitol Complex given its due place of pride.
Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 provides a useful base for regulating development and building activity in the entire UT of Chandigarh. Thus the reference area for planning constitutes 144 sq km which includes the 60 sectors in the sectoral grid as well as the periphery areas outside it.
Population
During the last 6 decades (1951-2011), Chandigarh has witnessed a population increase of more than forty four times with the absolute population increasing from 24,261 in 1951 to 10,54,686 in 2011.
| Year | Total Population | Decadal Absolute Variation of Population | Decadal Growth Rate (in%) |
| 1951 | 24261 | – | – |
| 1961 | 119881 | 95620 | 394.13 |
| 1971 | 257251 | 137370 | 114.59 |
| 1981 | 451610 | 194359 | 75.55 |
| 1991 | 642015 | 190405 | 42.16 |
| 2001 | 900635 | 258620 | 40.28 |
| 2011 | 1054686 | 154051 | 17.1 |
Source – Census of India
The growth rate of merely 17.10% between 2001-2011 is the slowest since its inception. This is perhaps due to the rapid pace of urbanization taking place in the neighbouring towns of Mohali, Panchkula, Zirakpur, Kalka, Kharar, etc. falling within the 16 km periphery control area.
The population density during the last 5 decades (1961-2011) has increased 9 fold, from 1051 to 9252 persons per sq. km. As per Chandigarh Master Plan 2031, Chandigarh shall continue to record higher densities with further population growth, which poses a challenge for maintaining the quality of life and providing basic & essential services even to its poorest residents as visioned by the city’s planners.
Population Projection
POPULATION PROJECTION OF CHANDIGARH UT BY VARIOUS METHODS:
| Sr. No. | Method | 2011 | 2021 | 2031 |
| 1 | Arithmetic Progression | 1054686 | 1241647 | 1428608 |
| 2 | Geometric Progression | 1054686 | 1474694 | 2061962 |
| 3 | Incremental Increase | 1054686 | 1272457 | 1521039 |
| 4 | Exponential | 1054686 | 1882540 | 3360200 |
| Average | 1054686 | 1467834 | 2092952 |
Taking various population projections as above into account, it will be realistic to assume that Chandigarh U.T will have a population of 13.5-14.5 lakhs by the year 2021 & 15-16 lakhs by the year 2031. Population for the Chandigarh U.T has also been projected based on the holding capacity of the area.
The total holding capacity of the U.T of Chandigarh has been worked out as 15.52 lakhs. While it may not be possible to make an accurate forecast, the expectation is that the UT’s population will range between 15-16 lakhs, by 2031 for which the provision of necessary infrastructure should be planned.
Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 entails that additional population will have to be diverted to the adjoining settlements by viewing the entire context of planning in the regional framework.
Land Use
Existing Land Use
Landuse for the city of Chandigarh was defined by the Plan prepared by Le Corbusier, based on the CIAM (Congress International de Architecture Modern) principles of the Functional City. These principles focused on segregation of four major functions:
- Living (the residential sectors)
- Working (the Capitol Complex, commercial /institutional buildings along Madhya Marg, Jan Marg, City Centre )
- Care of Body and Spirit (the Leisure Valley, open spaces and sector greens) and
- Circulation (the network of roads, the 7Vs).
Phases
The total area proposed to be covered is the entire area of 28169.61 acres comprising of Chandigarh Union Territory . The area includes the area falling under the Phase I ,Phase II and Phase III sectors besides the area under the periphery.
Considering the pattern of development followed in Chandigarh, the Existing LandUse Plan is being detailed out in two parts. Part I comprises of planned development included in the original plan (Phase I & II) and the subsequent developments made as part of the extended sectoral grid (Phase III ). The remaining landuse of the area falling in the periphery is being detailed out separately keeping in view the nature and context of development.
The details of areas falling under different phases and periphery are as under:
| CATEGORY | SECTORS | AREA (acres) | PERCENTAGE |
| Phase I | 1 TO 30 * | 9398.83 | 33.37 |
| Phase II | 31 TO 47** | 5158.76 | 18.31 |
| Phase III | 48 TO 56 (Part) |
1870.54 | 6.64 |
| Sub-Total | 16427.73 | 58.32 | |
| Remaining area of periphery | 11741.88 | 41.68 | |
| Grand total | 28170 | ||
*Includes the area of Industrial Area Phase I, Sukhna Lake, Golf Range.
**Includes the area under Industrial Phase II .
Proposed Land Use
Based on detailed studies, in depth analysis and looking at the future growth and development of Chandigarh, proposed Landuse Plan for the Chandigarh Union Territory has been evolved. While evolving this landuse plan, care has been taken to preserve the sectors which have already been planned and the landuses which have already been defined in the planning of the sectors.
Accordingly, no change is proposed in the landuse already defined in the sectors falling in Phase I, Phase II and Phase III. However, while retaining the broad landuses, the Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 proposes that in order to meet the requirements of basic infrastructure/amenities due to increase in population or any other contingency, the mechanism of redensification may be adopted.
Proposed Development
Out of the total land of 11,742 acres in the periphery, 3082 acres is vacant land which is considered for development. The proposed development in the periphery has been defined in 17 distinct pockets having a total area of 3082 acres.
| S.No. | Use | Area (acres) |
| 1 | Residential | 194.695 |
| 2 | Commercial | 141.46 |
| 3 | Transportation | 51.57 |
| 4 | Industrial / IT Parks | 283.56 |
| 5 | Public/ Semi-Public | 454.982 |
| 6 | Recreational | 389.88 |
| 7 | Agriculture | 673.858 |
| 8 | Public Utilities | 39.08 |
| 9 | Forest | 430.88 |
| 10 | Reserved | 308.835 |
| 11 | Vacant | 113.98 |
| Total | 3082.78 | |
Transportation
RITES has proposed an integrated multi-modal mass transport system consisting of metro rail, BRT, commuter rail system and normal city bus system for the Chandigarh Urban Complex and its linkages to nearby towns to meet the anticipated commuter travel needs.
Within Chandigarh Urban Complex
- Mass Transport System
- Metro System – 64.3 kms
- Bus Rapid Transport (BRT) System – 144.2 kms
- City Bus System
- Augmentation of Bus Fleet
- Bus Terminals
- Bus Shelters
- Additional Depots
- Inter-city Bus Terminal
- Road Infrastructure
- Parking Facilities
- Inter-modal Interchanges
- Integrated Freight Complexes
Outside Chandigarh Urban Complex
- Road Infrastructure
- Bypasses
- Road widening
- Commuter Rail System
- Bus Rapid Transit System
