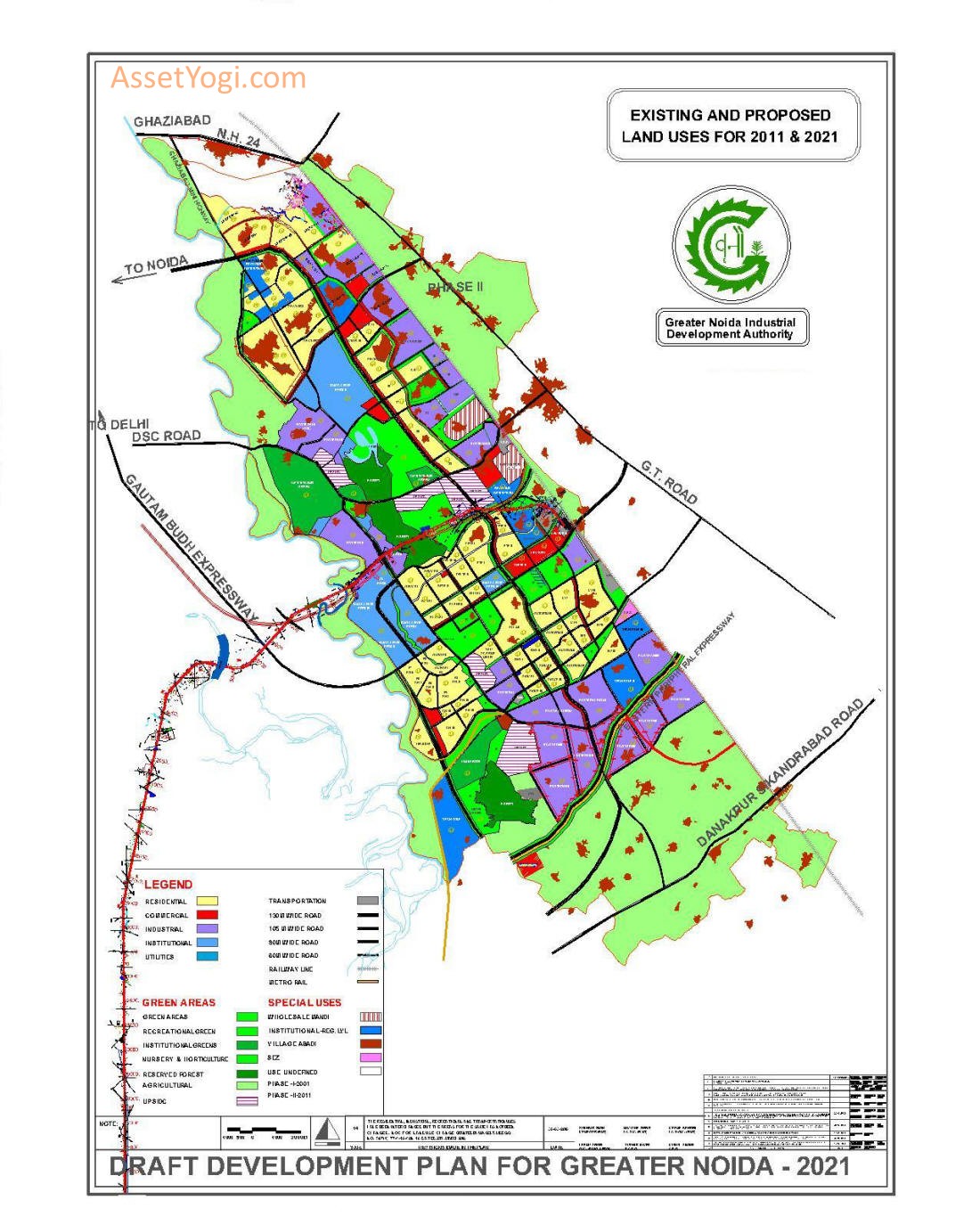
Greater Noida Master Plan 2021 has been prepared to provide vision & regulations for development and building activity in the Greater Noida Region of Uttar Pradesh. It envisages a population of 12 lakhs by 2021 for Greater Noida. Accordingly 22,255 hectares of land is allocated under the proposed land use by 2021 in greater noida master plan.
You can download the complete report for master development plan of greater noida and land use map from below. Check out the summary of Greater Noida master plan 2021, in case you don’t want to go through the complete master plan report. To share your opinions and suggestions, please use the comments section at the end.
Downloads
Download Greater Noida Master Plan 2021 Map and full report. You can also download the Noida-Greater noida Metro Plan Map.
Highlights – Greater Noida Master Plan 2021
INTRODUCTION
Greater Noida is a census town with a population of 100,000 in the Gautam Budh Nagar district of the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It comes under the purview of the National Capital Region (NCR) of India. Greater Noida is 48 km and one hour from New Delhi.
Development is managed by the Greater Noida Industrial Development Authority (GNIDA). Greater Noida is connected to Agra by the six-lane Yamuna Expressway. The annual Indian Grand Prix is held at the Buddh International Circuit which has helped putting the city firmly on the global map.
The new city of Greater Noida is located close to the National Capital of Delhi in the National Capital Region (NCR). It is situated in close proximity to Delhi at a distance of about 25 Kms from the border of Delhi (at Okhla Barrage).
The notified area of Greater Noida comprising of 124 villages and about 40000 Ha. of area is broadly bounded by National Highway 24 in the north-west, river Hindon in the western side and G.T. Road/Northern Railway main line to Calcutta on the eastern side.
It is abutting the areas of Noida on its western side and Ghaziabad on the northern side. Due to nearness to Delhi and both these towns being well developed the pressure for development is there on Greater Noida.
Noida extension is a part of Greater Noida, in Gautam Budh Nagar district of Uttar Pradesh and consists of 16 villages. All sectors under Noida Extension (Sector 1 to 4) are very much a part of the Greater Noida Industrial Development Authority (GNIDA).
Planning in Greater Noida
Greater Noida is planned to have excellent connectivity to the other parts of the region using Metro, road and rail. Systematic infrastructure developments and vision to create a residential and commercial spaces in the same region fueled its realty and commercial growth.
Planned IT parks and industries in this area along with innumerable housing projects are important avenues for providing employment in this region. Approval to the development master plan by NCR planning board has paved way for rapid infrastructure, social and cultural development in this area.
GNIDA declared its plans to extend the Noida City Centre line to Noida Extension with DMRC and further till BODAKI in PPP model to fuel the growth prospects in this area.
BACKGROUND
The creation of Greater Noida is an outcome of the intensive pressure of the National Capital of Delhi on its periphery. On the east of Delhi, abutting the border, is located the notified area of Noida which is a planned township. Just outside the notified area of Noida, the pressures for development around Delhi and DMA started manifesting in the form of haphazard growth by colonizers and speculative land dealings in the area.
The Government of Uttar Pradesh was concerned with unplanned growth in the area and initially declared it as notified area under U.P. Regulations of Building Operations Act, 1958 on 19th Sept., 1989, under U.P. Industrial Area Development Act, 1976.
Thereafter, the Government of Uttar Pradesh vide notification dated 28th January 1991 constituted Greater Noida Industrial Development Authority. The first Master Plan was prepared by the Authority in 1992 from School of Planning & Architecture as a consultant. The plan was for 5.00 lakhs population and was then revised in NCR Plan context in 1996 as Outline Development Plan 2001 for Surajpur-Kasna sub regional centres.
The NCR Plan-2021
The NCR Plan-2021 has been fianlised and notified on 17th September 2005. Greater Noida has been identified as a Metro Centre and lies on the Rest of NCR zone delineate in the NCR Plan-2021. As per the Plan, in the ‘Rest of NCR’ accelerated development of both urban and rural areas is proposed to continue.
Infrastructure is proposed to be substantially upgraded at local and regional level (both by Sate and Central Government) in order to induce the growth in these areas, specifically in the identified settlements i.e., Metro Centres and Regional Centres. This will make them more attractive for locating economic and allied activities and for attracting private sector investment.
These Centres are envisaged as powerful growth nodes to attract capital functions and activities and help in population dispersal from the National Capital. Because of their special functional status and size, a very high level of physical, social and economic infrastructure better than that in the Capital is required to be developed within these towns/complexes.
This would include efficient intra-urban mass transportation system as well as strong transport and communication linkages with Delhi, other Metro Centres and NCR towns. The objectives of NCR Plan-2021 for Planning Greater Noida as Metro Centre have been followed in preparation of Greater Noida Master Plan 2021.
POPULATION PROJECTION
Population projection for the urban area in the new town like Greater Noida cannot be simply done based on any conventional projection methods based on past trends of growth because in a new township almost the entire population, which is going to settle, is going to migrate from surrounding areas.
Hence, population projection is done with 3 methods and an average is considered for the final projections.
| Methods | Projected Population (Lakhs) | |
| 2011 | 2021 | |
| Method 1 (Average growth rate of neighbouring DMA towns method) |
6.6 | 12.74 |
| Method 2 (Industrial workforce method) |
6.06 | 11.7 |
| Method 3 (By area developed and allotted) |
4.96 | 9.57 |
For the final projection, the average for the above mentioned figures are taken which comes to 5.87 lakhs and 11.34 for the year 2011 and 2021 respectively. Apart from the urban population growth based on above mentioned methods, there is bound to be migration from the villages in the notified area (outside the urbanisable area) due to better living conditions in the urban area.
The rural population for the villages in notified area is projected to 3.15 lakhs. It is assumed that about 30% of the population will move to urban settlements and there will be an addition of 1.0 lakh in the population on this account. Hence the total projected population for the year 2011 comes to 6.87 lakhs rounded off to 7.0 lakhs.
Similarly, for the year 2021 assuming a decadal growth rate of 93%, the population will be 12.34 lakhs say 12.0 lakhs.
LAND USE PROJECTIONS
Land use is proposed in Greater Noida Master Plan 2021 by considering the population for two phases i.e. 7.0 lakh for first phase (2001-2011) and 12.0 lakh for second phase (2011-2021).
Land use Projections for 1st and 2nd phase (2001-2011)
As defined in the concept the city is being planned comparatively low population density with more open spaces . So density assumed for the two phases of development is 60 pph. As per the existing provisions for town density.
Present gross density of Greater Noida (2001) =300000/5076.55 = 59 pph say 60 pph.
Total population projected for first phase =700000
Total area proposed for first phase =13570
Land use projections for second phase (2011-2021)
Population projected for second phase = 12,00,000
Total area proposed for second phase =22255 hectares
Land use break up (including SEZ and Regional level Institutional area):
| Land use | 2001(ha) | %age | 2011(ha) | %age | 2021(ha) | %age |
| Residential | 1310 | 25.8 | 3000 | 22.10 | 5000 | 22.36 |
| Industrial | 1596.96 | 31.5 | 3027.3 |
|
4201.23 | 18.88 |
| Commercial | 99.74 | 2 | 720 | 5.30 | 1200 | 5.39 |
| Institutional | 570.63 | 11.2 | 2502.7 | 18.4 | 3473.99 | 15.51 |
| Green areas | 1361.9 | 26.8 | 3000 | 22.10 | 5000 | 22.36 |
| Transportation | 137.32 | 2.7 | 1280 | 9.45 | 3339.78 | 15.01 |
| SEZ | 40 | 0.3 | 40 | 0.78 | ||
| Total | 5075 | 100 | 13570 | 100 | 22255 | 100 |
Residential Area
Area proposed for residential use in the first phase (2001-2011) is 3000 hectares which is 22.10 % of total land use and it will accommodate the population of 7.0 lakh. Residential area proposed for the second phase (2011-2021) for the population of 12.0 lakh is 5000 hectares (22.36% of total land use).
This area has been worked out on the basis of gross residential density of about 230 ppha in the present plan for the first phase upto 2011. In the second phase of greater noida master plan 2021, the pressure on the land will increase due to decreasing the availability of land in Delhi and Noida and hence the gross residential density has been increased marginally to 240 ppha.
Area under residential use for LIG and EWS housing shall be provided while preparing detailed sector layout.
Industrial Area
At present industrial area is about 1600 ha. The industrial land is being disposed off at an average rate of 100 ha. Per year. Assuming a faster trend to continue for next forthcoming years (2001-2011) 1427.30 ha. ( i.e total land upto 2011 (2027.30 ha.). In the second phase (2011-2021) due to increasing pressure on land the average rate of allotment per year has been marginally increased to 120 ha. Per year and the land requirement works out to 1200 ha. (total land upto 2021 – 3800 ha.) The list of restricted industries in Greater Noida is enclosed at Annexure A.
The Institutional land use comprising of area for Govt./Semi Govt. and Private Institutions and offices, Regional level Institutions (IT and ITES use) and public utilities. The area break up for the same in greater noida master plan 2021 is proposed as follows:-
| S.No | Use | 2011 (Ha) |
Upto 2021 (Ha) |
| 1 | Govt-Semi Govt, Private institutions and offices | 1200 | 2050 |
| 2 | Regional level Institute (IT and ITES) | 1002.7 | 1002.7 |
| 3 | Public utilities | 200 | 350 |
| Total | 2502.7 | 3502.7 |
The activities permitted in these area are outlined in Chapter-10 on Zoning Regulations.
Green Areas
The land for Green area comprises of:-
- Recreational Green – 2016.0 Ha.
- Institutional Green – 1017.0 Ha.
- Parks and open spaces, green belts, Nursery and Horticulture 952.0 Ha.
- Reserved forest – 1015.0 Ha.
Transportation Areas
As per suggestion of chief town and country planner, UP Government, the transportation land use area has been increased to 15.01%. this has been achieved after including all regional linkages like, Eastern Peripheral Expressway, Orbital Rail, Ganga Expressway, Yamuna Expressway, Dedicated Freight Corridor, Northern Rail Link and other Roads of 45.0 mtr. width and more in institutional and Industrial areas.
- The percentage distribution of land under recreational and institutional use has been kept as per the provisions in the existing plan maintaining the character of industrial cum institutional city set in an environment of greenery and openness.
- The percentage of land under Transport and Commercial use has been increased in the greater noida master plan 2021 as the provisions for the same were not adequate in the ODP-2001.
Town Density
The Town density on the gross area 22255 Ha works out to about 56 person/Ha. The low town density is on account of the following:-
- The city has been planned as a lung space for the surrounding region, therefore a high percentage of area has been reserved for green area.
- Existence of large area of reserved forest within the Urban area.
- Being an industrial township, a high percentage of land is under industrial use. The industries require large chunks of land but being mechanized and capital intensive, have a very low workers density.
- High percentage of land under Institutional use providing large nos of Regional level Institutions serving not only the city but also the NCR region.
Therefore the proposed landuse and density of Greater Noida city has to be assessed viewed in light of the above and the objective to plan the city to provide for the inadequacies in the NCR Region and not as a Metro City in isolation.
TRANSPORT
A detailed Transport Master Plan has been prepared by RITES and salient features of the plan are as follows:
Road Linkages:
The major road linkages planned are—
- From Delhi and NOIDA—access via DND Flyway Toll Bridge to NOIDA-Greater Noida Expressway, which is proposed to be extended up to Agra (Taj Expressway).
- Link from Noida via Okhla Barrage road through the Master Plan road No.3 of Noida, extending it across river Hindon and providing access to the 130.0m wide road of Greater Noida.
- Connecting road from Eastern peripheral Expressway of NCR Plan at NH-24 interchange (to be finalized after finalization of alignment of the Expressway).
- Link from NH-24 to connect area on north of Entry road (industrial sector Ecotech-III).
- Link to surrounding areas of Uttar Pradesh shall be via NH-24 bypass in the northern side and from GT Road on eastern side of the area.
- A 130 m. wide road has been planned as backbone of the linear City for connecting its northern and southern parts and also Noida and Delhi.
Rail Linkages
- The Northern Railway main line from Delhi to Calcutta is abutting the Master Plan area. It is proposed to develop Boraki as a new railway station on this line for the City. A feasibility report for the same has been prepared by RITES and submitted to Railways. A rail link between Dadri and Tuglakabad is proposed, which will connect Greater Noida with the main railway lines in the East to Calcutta and West to Bombay.
- For movement of goods traffic Inland Container Depot has been located, which will be provided with rail linkage form Tuglakabad.
- There is proposal to have Transport hub at Boraki, which shall provide comprehensive facilities for integrate of passenger railway station, ISBT, Truck Terminal, etc.
Mass Rapid Transit System
A feasibility study has been carried out by RITES for developing a rail transit system between Noida and Greater Noida also serving the City of Greater Noida. Based on the results of transport demand forecast and system selection, a Light Rail Transit (LRT) system has been recommended. The LRT system shall be able to cater the future travel demand and shall supplement the bus system.
- Phase-1: NOIDA City Centre to GNIDA along Storm Drain, proposed SEZ, Gautam Buddha Expressway, Pari Chowk and along 105 m road upto proposed 130 m. road (about 29 km)—Costing about Rs. 2610 crores.
- Phase-2: GNIDA to NOIDA City Centre- Along 130 m. middle spine road, NOIDA Sec 52 (about 25 km) – costing about Rs. 2250 crores.
The final report for the study submitted by RITES is available as a separate document.
Public Transport Plan
A public transport system has been planned to serve the Intra-City’s traffic movement. The desired demand for bus passengers is projected at about 1.9 and 4.1 lakh trips in the year 2011 and 2021 respectively. A bus system has been proposed for intra-city movement in the greater noida master plan of 2021.
Sixteen bus routes have been proposed to cover the entire region and also to connect various other destinations like Noida, Ghaziabad, Delhi. Four bus terminals have been proposed at Kasna, near Dadri, near Knowledge Park-V and at Boraki in the transport hub.
Road Network
Hierarchy of road network:
- 130 m. wide main arterial road (Central Spine from North-West to South-East)
- 105 m. wide the Meridian road.
- 80 m. wide Promenade (S.K. Road) and road along kot escape.
- 75 m. wide Noida-Greater Noida Expressway
- 60 m. wide sector peripheral roads
- 45 m. wide DSC Road (existing) and road along railway line.
Typical cross sections for roads having various Right of Way (ROW) have been recommended. The provision for NMVs, bus lanes, pedestrian facilities, space for services etc. has been proposed in greater noida master plan of 2021. Typical junction designs have also been proposed for different types of road cross sections. The detailed cross sections are incorporated in the Transportation Master Plan.
To avoid heavy delays at rail-level crossings ROBs are prepared near Roopwas, Boraki, Gori Bachera, Sikandrabad crossing, LG factory, and sector Zeta-I.
